
The word vertigo is derived from the Latin phrase verto, which means “to revolve.”
Vertigo is a false sense of motion, spinning, or feeling of imbalance. Sufferers often call it dizziness, imbalance, light-headedness, or “chakkar aana” in Hindi. Vertigo symptoms often include nausea, vomiting, difficulty in focusing on moving objects, headaches, changes in hearing or ringing in the ears, and difficulty in concentration or unsteadiness while walking. It may worsen when you move your head. Their symptoms can come and go and can range from a few seconds to minutes, hours, or even days. Understanding the dizziness causes is essential to manage and treat the condition effectively.
15% of people have dizziness and balance disorders.

Vertigo is not a disease; it’s only a symptom. Therefore, suppressing the symptom is not the solution.
Proper vertigo diagnosis of what is causing vertigo/dizziness is possible only when the doctor makes a systematic evaluation. A neuro-otological (ear and brain) workup alone will help to find out if a vertigo patient is suffering from disorders like BPPV, Meniere’s Disease, Vestibular Neuritis, Labyrinthitis, Acoustic Neuroma, Otolith Dysfunction, Vestibular Migraine, Central Vestibulopathy, or psychogenic disorders—each presenting with distinct vertigo symptoms and dizziness causes.
Different disorders causing vertigo have different presentations and require diverse treatment protocols. A correct diagnosis will enable the doctor to offer the right vertigo treatment, which is the only way to give the patient lasting relief.


vertigo A false feeling of rotation or movement when you are actually not moving. It is not a disease per se, but a symptom of a disease in the inner ear or the brain. Individuals who have vertigo may say that it feels like the room is spinning, leaning, or swinging around them, when in reality nothing is.
Simply put, vertigo occurs when your brain receives conflicting information in the form of signals sent to it by your inner ear, eyes and body. This signal block gives an illusion that you are in transit but you are not.
Many people often use the terms vertigo and dizziness interchangeably, but they describe different sensations and have distinct underlying causes.
Vertigo is a specific type of dizziness that gives you the false sensation that you or your surroundings are spinning or moving. It often feels like you are rotating even when you are perfectly still. Common Vertigo symptoms include:
Vertigo is typically linked to problems in the inner ear or the vestibular system, such as Ben
ign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo (BPPV), Meniere’s disease, or vestibular neuritis.
Dizziness is a broader term that refers to sensations like feeling lightheaded, faint, unsteady, or disoriented. It does not always involve the spinning feeling associated with vertigo. Dizziness causes can include:
Unlike vertigo, dizziness is often linked to cardiovascular, neurological, or systemic issues rather than the balance organs in the inner ear.
| Feature | Vertigo | Dizziness |
| Sensation | Spinning or moving | Lightheadedness, faintness, imbalance |
| Primary Causes | Inner ear disorders | Blood pressure issues, dehydration, anxiety |
| Symptoms | Spinning, nausea, eye movements | Fainting, unsteadiness, disorientation |
Patients suffering from persistent or intermittent dizzy intervals of vertigo usually describe their symptoms as:









It is a disorder of the inner ear, characterized by episodes of hearing loss and fullness in one ear, tinnitus, and vertigo. Meniere’s Disease is caused by increased pressure of the inner ear fluid. If not treated timely, it can lead to progressive hearing loss. Vertigo symptoms in Meniere’s are intense and recurring.
Vestibular Neuritis is caused by a viral infection leading to inflammation of the vestibular nerve. This disturbs the balance function and causes dizziness. The symptom is accompanied by blurred vision, nausea, vomiting, and difficulty focusing during head movement. Early vestibular rehabilitation helps ensure rapid recovery. It is one of the common dizziness causes in viral infections.
Damage to the otolith organs (utricle and saccule) cause disequilibrium of the body and affects visual stability. Until recently, there was no precise method to check the impairment of otolith organs. But now Otolith disorders can be diagnosed with the Subjective Visual Vertical test and VEMP. Otolith stimulation through vestibular rehabilitation therapy works well in treating the disorder. Otolithic issues often present with persistent vertigo symptoms.
10% of the population is affected by a migraine, most of them are women. The most common presentation of a migraine is headaches. But in a vestibular migraine, the patient has dizziness which may be associated with headaches. A severe headache coupled with dizziness indicates a vestibular migraine. Along with the spinning sensation associated with headaches, motion sickness and hypersensitivity to light and sound prominently show up in the patient. A vestibular migraine is controlled with diet and lifestyle modifications. In cases of frequent dizzy spells, migraine prophylaxis is prescribed. It is one of the lesser-known dizziness causes.
The unusual movements of carbonate crystals from their chamber into fluid-filled semicircular canals disturbs the way the balance nerve senses gravity and adjusts its movement. The result is vertigo or the sensation of spinning. BPPV is a common cause of vertigo. It is seen more frequently in the older population, after an ear infection, head injury, surgery or after prolonged rest. But often the trigger is unknown. The canalith repositioning exercises are the best method to cure dizziness caused by BPPV in which the offending particles are repositioned according to the type of BPPV by manoeuvres like Epley Manoeuvre, Semont Manoeuvre etc. BPPV is one of the most treatable dizziness causes and presents with classic vertigo symptoms.
The infection causes labyrinthitis in the labyrinth of the inner ear leading to vertigo, hearing loss and tinnitus. The difference between labyrinthitis and vestibular neuritis is; in labyrinthitis both vestibular and cochlear nerves are affected and cause dizziness, ringing in the ear and hearing loss. While in Vestibular neuritis only vestibular nerve is affected leading to vertigo but the hearing ability is not affected. Labyrinthitis causes severe vertigo symptoms that may last for days! Vestibular suppressants may be prescribed by the doctors to treat dizziness and its associated symptoms, for a very short duration of 3 to 5 days. Vestibular rehabilitation should be started at the earliest to ensure rapid recovery.
Dizziness, fullness in the ear, vertigo spells are the symptoms of perilymph fistula. A small tear in the fluid-filled inner ear causes fluid to leak into the middle ear. This leakage disturbs the equilibrium and leads to vertigo spells, especially when the patient does straining activities or coughs vigorously. This condition may also lead to tinnitus and hearing loss. Videonystagmography (VNG) and vestibular examination help diagnose the presence of the perilymph fistula.
The compression of the vestibular nerve due to an inflamed blood vessel, radiation, surgery, or vestibular neuritis may cause vestibular paroxysmia. Microvascular compression is the most common reason for vestibular paroxysmia. The patient may have frequent short spells of vertigo episodes recurring throughout the day. VNG/ ENG and MRI scanning are recommended to diagnose Vestibular paroxysmia.
A rare condition of SSCD may occur as a result of thinning, or damage to the bony part of the labyrinth. It affects the patient’s hearing ability too. Natural coughing or sneezing can trigger dizziness in this condition. These patients have an extreme sensitivity to loud sound. VNG guided Valsalva manoeuvre, VEMP and CT scan of the temporal bone confirms SSCD. The treatment for SSCD is to avoid actions which aggravate dizziness. Surgical repair of the bony dehiscence is advocated for lasting results. SSCD frequently causes vertigo symptoms in response to sound or pressure changes.
The patient experiences a continuous rocking or sense of motion as a result of long travel, either by ship or aeroplane. Some individuals may develop MdDs even without exposure to long travel. A thorough vestibular evaluation and studying the history of the patient can diagnose MdDS. Antidepressant medication is prescribed to treat the swaying sensation. Vestibular rehabilitation treatment is the best technique to treat MdDS. Virtual reality training is also advised for these patients.
Acoustic neuroma is a noncancerous growth on the balance nerve which causes unsteadiness, dizziness, facial numbness or tingling sensation, change in taste etc. A tumour grows slowly, and hence the patient often does not notice the symptoms. However, it may prove life-threatening if a tumour grows big enough to press on the brain stem. Surgery and radiation are widely used methods to treat acoustic neuroma.
Multiple sclerosis is an autoimmune disorder in which the protective myelin shield of the nerve cells get damaged hampering signal transmission to the brain. Difficulty in focusing, visual problems, vertigo spells and unsteadiness are some of the symptoms of multiple sclerosis. Spinal tap, VNG and MRI brain are advised in the evaluation to confirm multiple sclerosis. MS is a neurological condition with many complex dizziness causes, including central vertigo symptoms.
Vertigo is a feeling that everything around you is spinning, even when you’re standing still. There are two main types of vertigo:
This kind happens when there’s a problem in your inner ear, which helps with balance. Some common causes are:
Symptoms: Spinning sensation, dizziness when moving your head, ringing in the ears, feeling off balance.
This type is caused by problems in your brain, especially areas that control balance. It can happen due to:
Symptoms: Dizziness along with other signs like trouble speaking, muscle weakness, or trouble seeing clearly.
Sometimes vertigo doesn’t just happen on its own. It can be linked to other health problems in your body. Here are two important ones to know about:
In conditions like vestibular migraines, the brain reacts differently to movement, which can lead to a cycle of feeling dizzy and anxious at the same time.
Vertigo Type | Key Differentiator | First-Line Treatment |
BPPV (Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo) | Triggered by specific head movements; short, intense episodes | Canalith repositioning maneuvers (e.g., Epley) |
Vestibular Neuritis | Sudden onset; associated with viral infection; no hearing loss | Vestibular suppressants; corticosteroids |
Labyrinthitis | Similar to neuritis but includes hearing loss | Vestibular suppressants; antibiotics if bacterial |
Ménière’s Disease | Recurrent vertigo with hearing loss, tinnitus, ear fullness | Low-salt diet; diuretics; vestibular suppressants |
Vestibular Migraine | Associated with migraine symptoms (light/sound sensitivity) | Migraine prophylaxis; lifestyle modification |
Central Vertigo | Originates from brain (stroke, Multiple Sclerosis); may have neurological signs | Treat underlying cause; neurology referral |


There are various tests to diagnose vertigo and its cause.
NeuroEquilibrium is a leader in using cutting-edge technology to conduct a proper vertigo test to identify the underlying dizziness causes and vertigo symptoms. Advanced Vertigo and Balance Clinics worldwide use ultra-modern differential dizziness diagnosing devices to evaluate vertigo symptoms, dizziness causes, and the severity of dizzy spells in real-time.
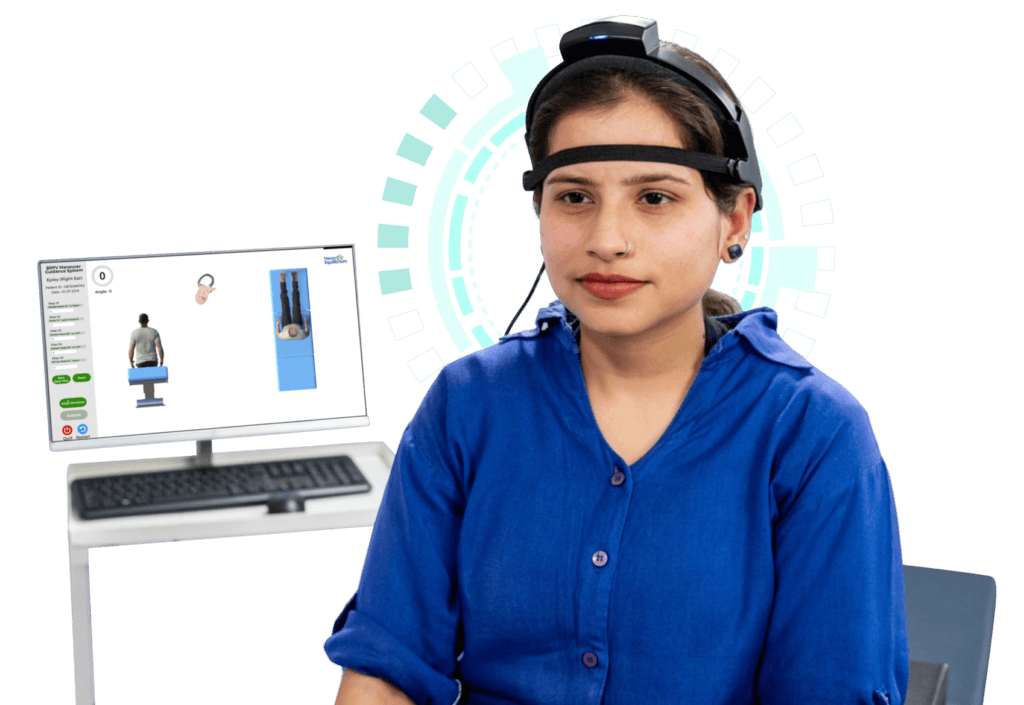

The doctor will look for any abnormal eye movements and ascertain that the ability to follow objects is normal. The doctor evaluates the involuntary eye-movements (nystagmus) of the patient. The rapid eye movements induced due to head maneuvers by the doctor may suggest in which ear the problem lies, helping to further pinpoint dizziness causes.
Tests are done on diagnostic devices such as Videonystagmography (VNG), Craniocorpography (CCG), Subjective Visual Vertical (SVV), computerized Dynamic Visual Acuity (DVA), and VEMP to identify the dizziness causes and the source of the balance disorder in the patient.
The frequency and severity along with the associated vertigo symptoms need to be considered for appropriate treatment of each patient.


Most people do not believe that their condition of imbalance can be cured. But fortunately, vertigo is curable. It is essential to get timely vertigo treatment to return to a healthy life as soon as possible. Here are a few ways:
Vertigo is only a symptom. Diagnosis of the underlying cause using various diagnostic tests like VNG etc. is essential for correct treatment.
Patients aksar poochte hain: “Chakkar kyun aata hai aur iska ilaj kya hai?”
Dizziness causes and treatment hamesha ek saath samajhna zaroori hota hai.
Example mapping:
Jab tak dizziness ka reason clear nahi hota, tab tak sahi treatment possible nahi hota.
Haan. Dizziness treatment effective hota hai jab:
Most cases of dizziness aur giddiness treatable hote hain, aur surgery sirf rare situations mein chahiye hoti hai.
Vertigo treatment in Hindi samajhna patients ke liye bahut madadgaar hota hai.
Isliye sirf dawa lena kaafi nahi hota.
Giddiness treatment tab zaroori hota hai jab:
Giddiness ka treatment cause-based hota hai, na ki ek hi medicine se sab theek hota hai.
Agar dizziness ke saath yeh symptoms ho, turant doctor se milna chahiye:
Yeh signs central vertigo ya neurological emergency ho sakte hain.
Some things can make you more likely to get vertigo, including:
If you suddenly feel dizzy or like the room is spinning, here’s what you can do:
If you get vertigo often, some small changes in your daily routine can help:
Dizziness, giddiness aur vertigo alag-alag feel ho sakte hain, lekin sahi diagnosis ke baad inka treatment possible hai.
Dizziness reasons and treatment ko ek saath samajhna hi long-term relief ka raasta hai.
What to take in case of dizziness relies on the cause. Non-prescription drugs, such as meclizine or dimenhydrinate, could be useful in case of dizziness during motion or inner ear dizziness. Mild symptoms may be alleviated by ginger tea or in the form of capsules. It is also important to be properly hydrated. When the dizziness is frequent, severe, or unexplained, one should inform a medical expert and then take medication.
To prevent the dizzy feeling, you need to sit or lie down immediately and prevent a sudden movement. Slow, deep breaths may be used when anxiety is one of the triggers. Episodes are usually decreased by drinking water, eating frequently, and getting more sleep. In case of persistent dizziness or balance issues, expert help of specialists, including those at Neuroequillibrium, is necessary to determine the cause of it and provide the appropriate treatment.
Natural medicine is the most effective treatment of dizziness, depending on the cause. Ginger is popular as a treatment of dizziness caused by nausea and motion sickness. Lightheadedness can be prevented by adequate hydration, regular meals and steady blood sugar. These mild cases of non-serious symptoms can also be managed by gentle head and neck movements, relaxation, and caffeine or alcohol avoidance.
Electrolytes may be used to treat dizziness when it is due to dehydration, excessive sweating, vomiting, or diarrhea. Sodium and potassium containing drinks can be used to restore fluid levels and enhance circulation. Nonetheless, electrolytes will not be effective in cases of dizziness due to inner ear complications, low blood pressure and nervous disorders. In case of the persistence of the symptoms even after the proper hydration, further medical examination is suggested.
Dizziness can be a major cause of a serious problem when it strikes abruptly, or is extreme as well as being accompanied with chest pain, weakness, numbness, slurred speech, vision loss or fainting. These are symptoms that may suggest stroke, heart diseases or nervous conditions. Relentless or unaccountable dizziness must be considered with formally trained experts, including clinicians at Neuroequillibrium, to exclude the underlying factors.
Corporate Office:
140, Shrigopal Nagar, Gopalpura Bypass Road, Jaipur 302018, Rajasthan, India
Manufacturing Site:
1st Floor, Plot No.3, Pooja Tower, Muktanand Nagar, Gopal pura Mode, Jaipur, Rajasthan 302018
All rights reserved © 2026 NeuroEquilibrium Diagnostic Systems Pvt Ltd.
Vertigo Clinic in Ujjain | Vertigo Clinic in Barwani | Vertigo Clinic in Patna | Vertigo Clinic in Miraj | Vertigo Clinic in Kolhapur | Vertigo Clinic in Nashik | Vertigo Clinic in Jaysingpur | Vertigo Clinic in Amravati | Vertigo Clinic in Solapur | Vertigo Clinic in Pune | Vertigo Clinic in Aurangabad | Vertigo Clinic in Nagpur | Vertigo Clinic in Sagar | Vertigo Clinic in Indore | Vertigo Clinic in Jabalpur | Vertigo Clinic in Bhopal | Vertigo Clinic in Bilaspur | Vertigo Clinic in Ahmedabad | Vertigo Clinic in Vadodara | Vertigo Clinic in Surat | Vertigo Clinic in Navi Mumbai | Vertigo Clinic in Thane | Vertigo Clinic in Mumbai | Vertigo Clinic in Palghar | Vertigo Clinic in Jaipur | Vertigo Clinic in Sriganganagar | Vertigo Clinic in Alwar | Vertigo Clinic in Kota | Vertigo Clinic in Udaipur | Vertigo Clinic in Lucknow | Vertigo Clinic in Prayagraj | Vertigo Clinic in Varanasi | Vertigo Clinic in Gurgaon | Vertigo Clinic in Dehradun | Vertigo Clinic in Rohtak | Vertigo Clinic in Amritsar | Vertigo Clinic in Ludhiana | Vertigo Clinic in Greater Noida | Vertigo Clinic in Delhi | Vertigo Clinic in Kannur | Vertigo Clinic in Trichur | Vertigo Clinic in Cochin | Vertigo Clinic in Coimbatore | Vertigo Clinic in Tiruppur | Vertigo Clinic in Chennai | Vertigo Clinic in Hosur | Vertigo Clinic in Bangalore | Vertigo Clinic in Mangalore | Vertigo Clinic in Hyderabad | Vertigo Clinic in Sangli